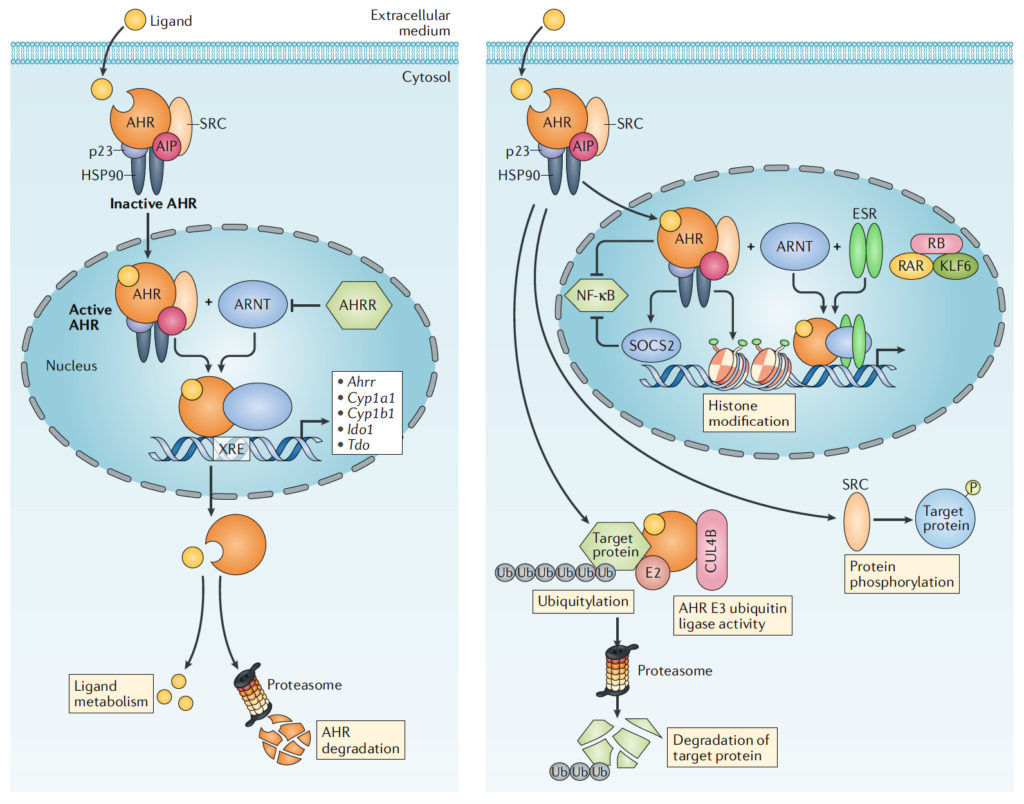
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AHR) is a pivotal protein that belongs to PAS [PER (periodic circadian protein)-ARNT(AHR nuclear translocator)-SIM (single-minded protein)] domain-containing receptor superfamily. This group of proteins play a central role in regulating cellular homeostasis by sensing endogenous (e.g. redox status and oxygen partial pressure) and exogenous stimuli (e.g. toxic aromatic hydrocarbons), and AHR, in particular, is recently emerging as an important gear of the machinery that regulates inflammation in the gut-brain axis (see here). The endogenous ligands for AHR include, mostly, triptophan derivatives which are either produced by endogenous metabolic pathways or by the commensal microbiota, which -on the other hand- can also produce other distinct molecules that possess AHR agonistic activity and are involved in a series of immunoregolatory functions (e.g. they can limit intestinal inflammation).
In this review, Veit Rothammer and Francisco Quintana cover the many facets of the complex network that is governed by AHR and his involvement in the regulation of the immune responses.